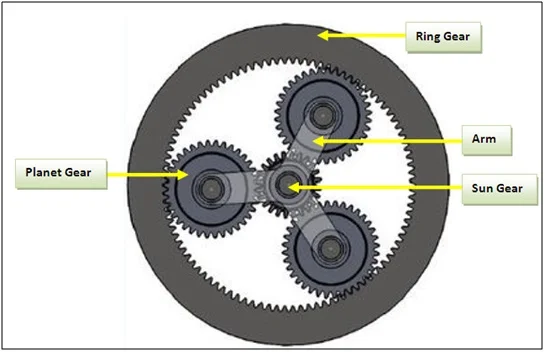
apologies for loss of some formatting
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Differential_(mechanical_device)
There are many claims to the invention of the differential gear, but it is possible that it was known, at least in some places, in ancient times. Confirmed historical milestones of the differential include:
100 BC–70 BC: The Antikythera mechanism has been dated to this period. It was discovered in 1902 on a shipwreck by sponge divers, and modern research suggests that it used a differential gear to determine the angle between the ecliptic positions of the Sun and Moon, and thus the phase of the Moon.
c. 250 AD: Chinese engineer Ma Jun creates the first well-documented south-pointing chariot, a precursor to the compass that uses differential gears to discern direction rather than a magnet.
1720: Joseph Williamson uses a differential gear in a clock.
1810: Rudolph Ackermann of Germany invents a four-wheel steering system for carriages, which some later writers mistakenly report as a differential.
1827: modern automotive differential patented by watchmaker Onésiphore Pecqueur (1792–1852) of the Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers in France for use on a steam wagon.
1832: Richard Roberts of England patents “gear of compensation”, a differential for road locomotives.
1874: Aveling and Porter of Rochester, Kent list a crane locomotive in their catalogue fitted with their patent differential gear on the rear axle.
1876: James Starley of Coventry invents chain-drive differential for use on bicycles; invention later used on automobiles by Karl Benz.
1897: first use of differential on an Australian steam car by David Shearer.
1958: Vernon Gleasman patents the Torsen dual-drive differential, a type of limited-slip differential that relies solely on the action of gearing, instead of a combination of clutches and gears.