This chart compares resolutions from different instruments.
The smaller the circle ther better.
This study is LoLSS.
The EMU study is from Murcheson in Western Australia,

The lower the frequency, the higher the redshift, so LoLSS sees objects that are further away than those from EMU.
But it can’t see objects that are as faint as EMU can see.
LOFAR will see: (https://www.aanda.org/articles/aa/full_html/2021/04/aa40316-21/aa40316-21.html)
- Distant galaxies and quasars
- Galaxy clusters and large-scale structure
- Radio-loud AGN
- Galaxies
- The Milky Way
- Stars and exoplanets – eg. anomalously active stars and close binaries
- Ionosphere
“In order to mitigate the consequences of poor ionospheric conditions: during each observation we simultaneously place three beams on three target fields for one hour.”
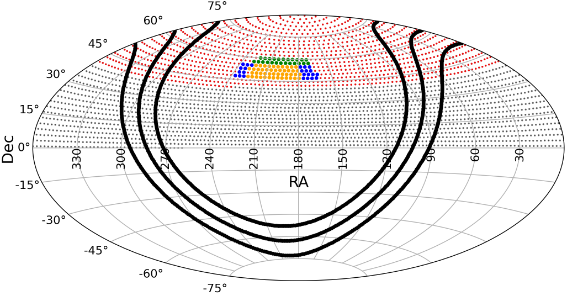
Current and planned sky coverage. The current area processed will be extended enormously.
Astrometric accuracy is about 2.5 arc seconds (which is darn good).
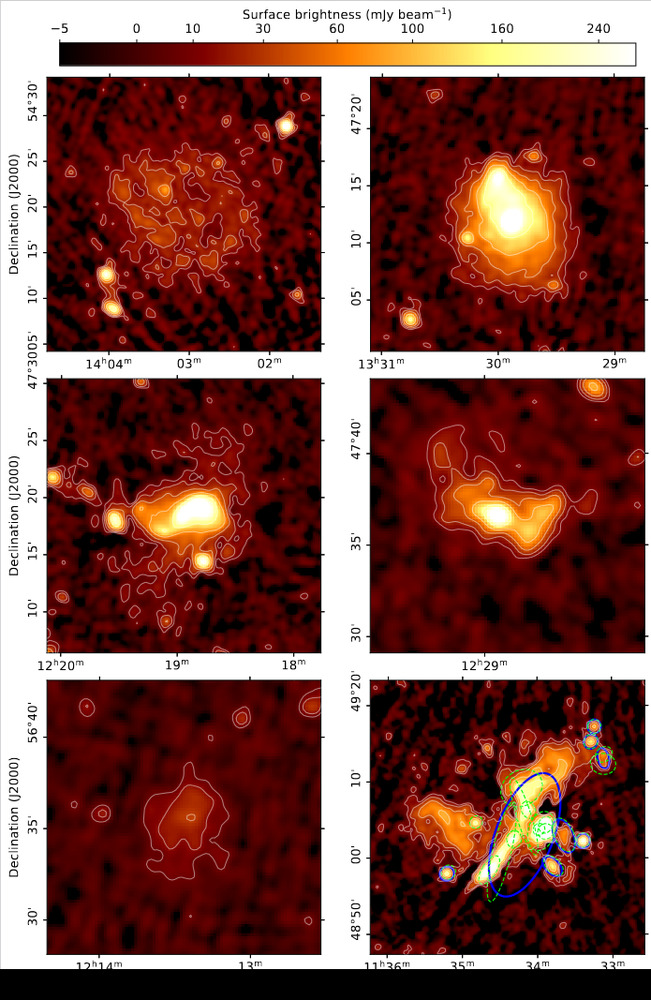
Extended sources, eg. multiple black holes, extended galaxies, gravitational lensing. Examples.