https://blogs.nasa.gov/webb/2022/06/23/webbs-nirspec-acquires-multiple-targets/
The Webb team has now approved 10 out of 17 science instrument modes; since last week we added (14) MIRI imaging, (2) NIRCam wide-field slitless spectroscopy, and our final NIRISS mode, (1) single-object slitless spectroscopy. As we ramp down the final commissioning activities, some openings in the schedule have appeared. The team has started to take some of the first science data, getting it ready to release starting July 12, 2022, which will mark the official end of commissioning Webb and the start of routine science operations.
How Webb gets the targets lined up for observation with the NIRSpec instrument
The Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) is the instrument on the Webb telescope that observes spectra of astrophysical and planetary objects at near infrared wavelengths. The NIRSpec Grating Wheel Assembly (GWA) uses diffraction gratings or a prism to separate the wavelengths of incoming light into a spectrum.
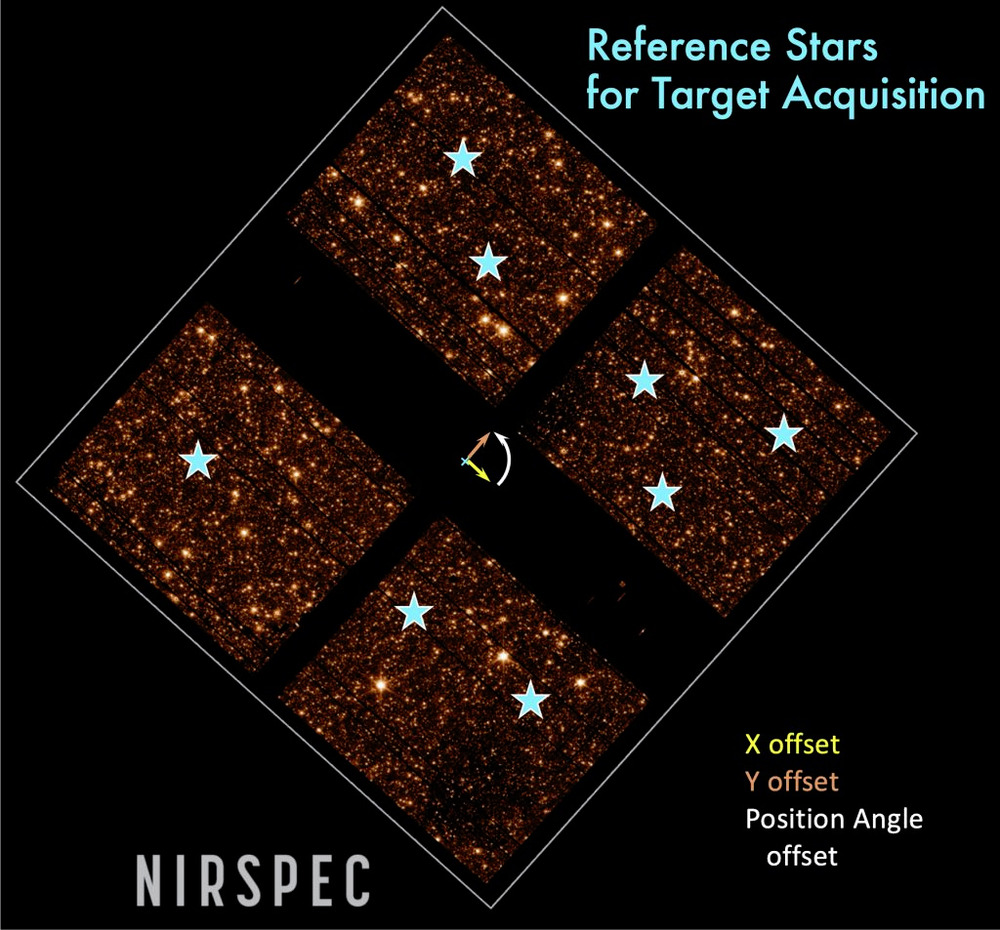
In addition to the gratings and a prism, the NIRSpec GWA also has a mirror that is primarily used to ‘acquire’ targets – to image them and place them at the proper locations in the instrument to observe a spectrum. NIRSpec has two methods for target acquisition (TA): the Wide Aperture Target Acquisition (WATA) and the Micro-Shutter Assembly (MSA) -based Target Acquisition (MSATA).
The WATA process takes an image of a single astrophysical target through the wide ‘S1600A1’ fixed slit to determine its position on the sky as seen through the instrument. The software on-board the Webb telescope autonomously calculates an offset to move the telescope and accurately position this target.
NIRSpec includes the multi-object spectroscopy (MOS) mode, where spectra of dozens to hundreds of science targets will be observed at one time. This requires specialized apertures that can be configured by opening and closing specific tiny doorways (microshutters) of the 250,000 total that are arranged in a rectangular grid in the MSA, allowing individual targets to be observed with little contamination from nearby objects or background light.
Wow!
To allow accurate correction of the observed spectra for the centering of each source in its shutter, this process must place the MOS science targets across the full span of the NIRSpec field of view with an accuracy of just 20 milli-arcseconds.
A simulation of target acquisition