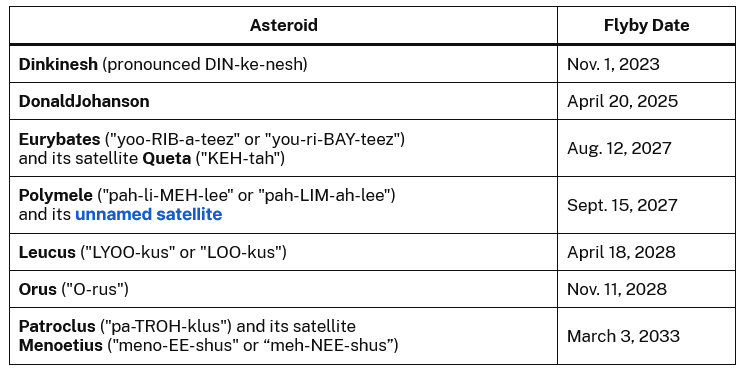
mollwollfumble said:
https://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap231104.html


More on the Lucy spacecraft. https://science.nasa.gov/mission/the-lucy-spacecraft/
“The Lucy LOng Range Reconnaissance Imager L’LORRI, is Lucy’s most sensitive and highest resolution camera. This black-and-white camera is a type of Ritchey–Chrétien telescope, the same basic design as the Hubble Space Telescope. Light travels down the tube and is reflected by the hyperbolic primary mirror, then travels back up the tube and is reflected by the hyperbolic secondary mirror.The secondary mirror focuses the light through an opening in the primary mirror. It then passes through a set of lenses. The image is recorded with a CCD.
“From 1,000 km away, L’LORRI will be able to clearly see craters with a diameter of 70 metres. It does not use optical filters. L’LORRI has no moving parts, not even a focusing mechanism, which reduces risk. Most of L’LORRI’s optical system is made of silicon carbide. The instrument is based on New Horizons’ LORRI instrument, which collected most of the incredibly detailed images of Pluto. A few changes were made to New Horizons’ LORRI for the Lucy mission (such as replacing its composite baffle with stronger aluminum, adding a second electronic pathway and more memory).”
“L’Ralph will search the Trojan asteroids’ surfaces for organic compounds, ices, and hydrated minerals, and its images will help us determine the Trojans’ surface compositions. L’ Ralph is actually two instruments in one — MVIC (Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera), a color visible imager, and LEISA (Linear Etalon Imaging Spectral Array), an infrared spectrometer. A beamsplitter inside sends the infrared light to LEISA and reflects the visible light to MVIC.
MVIC has five color bands that cover the visible to near infrared spectrum.
“The bands are chosen to help scientists identify compositional elements on the surfaces. For example, the phyllosilicate band is sensitive to phyllosilicates, a kind of hydrated mineral scientists expect to find.”
“MVIC uses six CCDs arrays, each with up to 64 rows of 5,000 pixels each.”
“LEISA contains a linear etalon, a thin, slightly sloped, transmitting layer of sapphire surrounded by a pair of reflective surfaces, slightly sloped on one side, that separates light into a spectrum, like a prism.”
“Because the images L’Ralph will take are so large, it has 256 gigabits of onboard memory. L’Ralph is based on the New Horizons instrument Ralph, as well as OSIRIS-REx’s OVIRS. Ralph gathered New Horizons’ incredible color images of Pluto”.
“The Lucy Thermal Emission Spectrometer (L’TES) detects far infrared radiation, using a telescope with diameter 15.2 cm to focus the incoming energy onto a small detector. In this way, L’TES acts like a remote thermometer. L’TES is not an imager.
“Lucy has a 2 m wide high gain antenna which will serve as the primary communications relay between the spacecraft and Earth. The team will also be able to use small velocity-induced shifts in the received radio frequency (the Doppler effect) to determine the masses of these never-before-visited space objects.
“Lucy will use its terminal tracking camera (T2CAM) to help navigate the spacecraft and track the asteroids during encounters. In addition to keeping the asteroids in the field of view of the main instruments, T2CAM will take wide-field images of the asteroids to better ascertain their shapes, and thus to determine the density.