(Disclaimer – clade and species names are subject to change without warning)
Cat Origins.
Where do cats come from? Do they come from Africa, Asia, America, Europe? Are they multi-regional? And by “cats” I mean the domestic cat, felinae, panthera and felidae in general. There are currently accepted to be 41 species of cat, umpteen subspecies, and umpteen extinct species.
Start with the domestic cat. Felis catus.
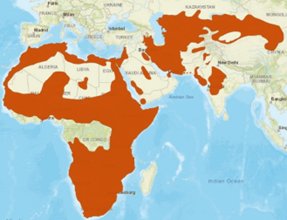
The domestic cat originated recently from Near-Eastern and Egyptian populations of the African wildcat, Felis lybica. Domestication occurred in the Near East. The African wildcat distribution looks like this, which is typical for an out-of-Africa species (like the lion).
The domestic cat did not come directly from the European wildcat F. silvestris.
Felis catus, F. lybica, F. silvestris form a clade with the Chinese mountain cat Felis bieti. It wasn’t until the year 2017 that these were accepted as different species.
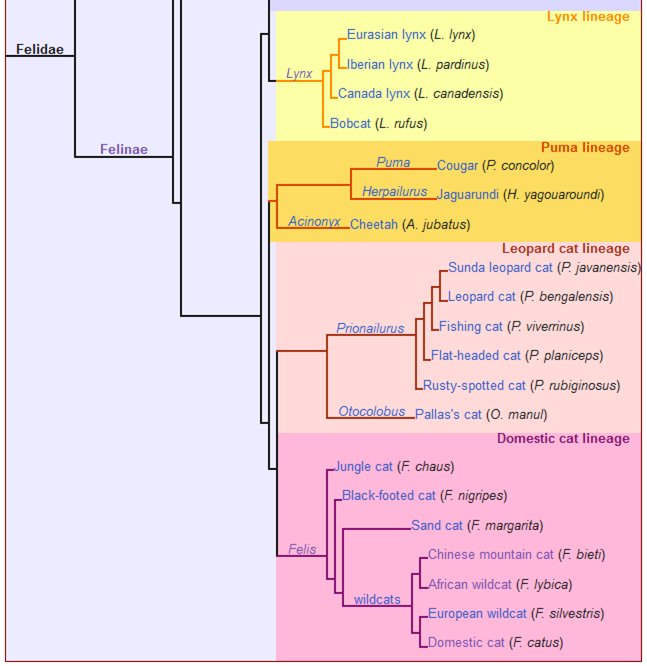
The next up contains the genera Felis, Otocolobus (Pallas’s cat) and Prionailurus (5 species including the Leopard cat and Fishing cat). These three genera split of from the rest of the Felinae some time between 3.04 to 0.99 million years ago in Eurasia. Image of Pallas’s cat.

The rest of the Felinae include 9 extant genera, Cheetah, Caracal, Catopuma, Jaguarundi, Serval, Leopardus (8 species including ocelot), Lynx, Marbled Cat, and Puma (Cougar). These split off from the rest of the Felidae some 11.5 million years ago. Individual Felinae genera split off between 10.67 and 4.23 million years ago. And six or so extinct genera.
The clade that contains Felis, Pallas’s cat and Fishing cat, is adjacent to the clade that contains Puma, Jaguarundi and Cheetah. In addition to the Americas, Puma ancestors have also been found in the countries France and Georgia.
The next most distant is the Lynx genus. Found in North America, Spain, and as far east as Siberia.
Then the Leopardus (Ocelot) genus. All 8 species are from South America.
Then the Caracal genus. Native to Africa and the Middle East.
Then the Catopuma genus from South-east Asia.
And a couple of extinct genera, Pardofelis from North America and Leptofelis from Spain.
Which brings us to the end of the Felinae. Can I get a geographic trajectory for the origin of Felinae genera? Not easily.
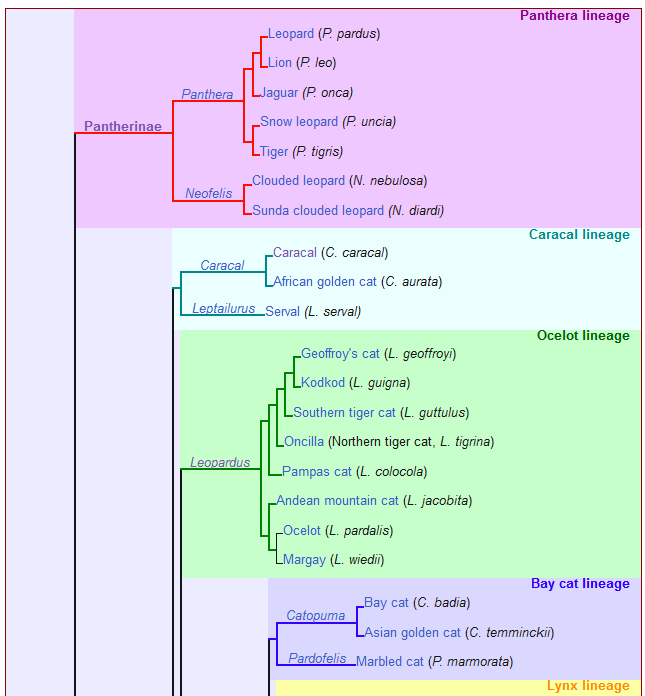
The other half of the extant cats is the Pantherinae. These are the big cats that can roar.
As said above, the Pantherinae split off from the Felinae some 11.5 million years ago. The Pantherinae genetically diverged from a common ancestor between 9.32 to 4.47 million years ago. There are seven extant species within the Pantherinae. (I bet you can only name six of them). The seventh is the Sunda Clouded Leopard, Neofelis diardi, that lives in Borneo and Sumatra. The Panthera is the part of the Pantherinae that excludes the two Clouded Leopard species.
Panthera blytheae is the oldest known fossil Panthera. It dates from 5.95 to 4.1 million years ago. The fossils were found in Tibet.
That’s all the extant cat species. But there are also extinct cat species going back further in time, including everyone’s favourite extinct cat – Smilodon.

Let’s see if I can get a time-line starting from the other end, from Carnivora.
There are at least 279 species of Carnivora. These are the obligatory meat eaters and exclude omnivores such as the bear and human. The seals split off first, and the remainder can be divided into two suborders, the Feliformia, containing the “cat-like” animals; and the Caniformia, containing the “dog-like” animals. The Caniformia have more teeth and the Feliformia fewer teeth. The Caniformia were ground-living and the Feliformia lived in trees.
The oldest known carnivoran line mammals (Miacoidea) appeared in North America 60 million years ago. They became true carnivores by 51.88 million years ago. These early carnivores resembled weasles. The split between Feliformia and Caniformia occurred 42 million years ago.
The extant Feliformia include only the cats and allies, hyenas and allies, mongooses and allies, and the civets. Extinct Feliformia include the false sabre-tooth cats. The ancestor of the cats and allies split off 34 million years ago. On the side branch, Hyenas and allies first appeared 22 million years ago.
The cats and allies are the Felidae. The first extant animals to split from these catlike animals were the Linsangs (2 species). They are not considered cats. The Linsangs split from the cats somewhere between 16 and 11.6 million years ago. Linsang image:

What else happened between 34 million years ago and 11.6 million years ago? Rather a lot, actually. At least six genera of extinct cat-like animals, containing at least fifteen species.