From a ‘The Atlantic’ email newsletter:
‘A Huge Financial Shock’
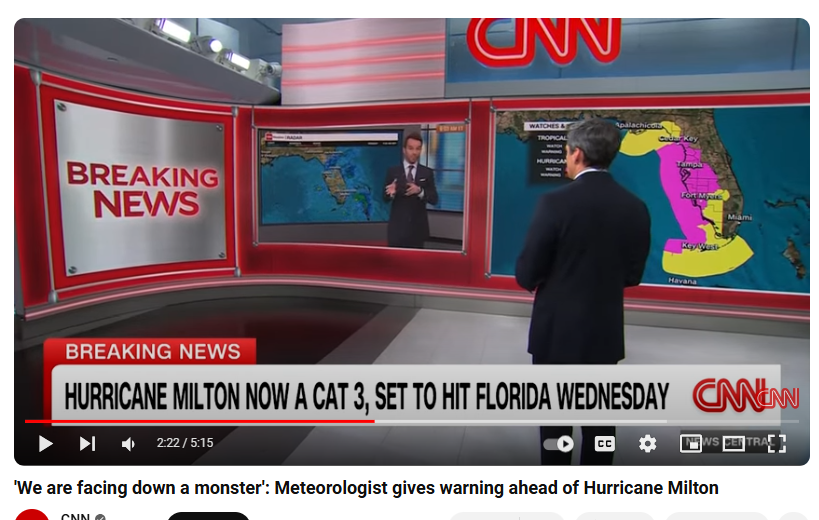
Western North Carolina lies hundreds of miles inland from any coast. The counties around the Blue Ridge Mountains sit at high elevations, away from the dense flood zones along the Atlantic. The idea that more than a foot of rain would rapidly overwhelm the region, sweeping up homes and ripping up vegetation, seemed almost unthinkable. But a week after Hurricane Helene made landfall, at least 200 people have died, and the death toll is expected to rise as the floodwaters recede and the debris clears. Many inland residents in North Carolina have never experienced flooding like this in their lifetime, and only a sliver have the flood insurance necessary to help them rebuild.
Flood insurance isn’t included in homeowner’s insurance, and Americans are generally not required to buy it. (One exception is the homeowners who live in high-risk areas, who must purchase flood insurance to get a federally backed mortgage.) Without this special coverage, floods can be “a huge financial shock to households,” Carolyn Kousky, the associate vice president for economics and policy at the Environmental Defense Fund, told me. Those living in storm-torn areas without coverage are looking at a massive list of expenses—home repairs, debris removal, temporary lodging—that they may have to pay for out of pocket after Helene. Still, just a tiny share of homeowners currently own flood insurance. Most of the North Carolina counties hit hard by Helene did not fall within high-risk areas on flood maps from the Federal Emergency Management Agency; one estimate found that less than 2.5 percent of homeowners in the region have flood insurance—and that number is even lower in some counties.
“In a perfect world, everyone with some degree of flood risk could and would carry flood insurance on their homes,” my colleague Zoë Schlanger, who covers climate change, told me. But the reality is that even some of the residents in flood-prone areas do not buy the plans because they are so expensive. The average premium cost $700 a year in 2019, but that number can reach the thousands for some coastal communities. Lower-income residents face an especially daunting situation: They are less likely to be able to afford flood insurance, and they also have less money on hand to rebuild.
Many people assume that they face little risk if they aren’t living in an area included in high-risk zones on FEMA’s flood maps, Sarah Pralle, a political-science professor at the Maxwell School at Syracuse University, told me. But FEMA’s maps don’t capture the full picture of flood risk. They are drawn “based on the assumption that the past will help us predict the future. In a rapidly changing climate, that’s not the case.” The maps can quickly become outdated as climate risks evolve, she noted, and don’t take into account fluvial flooding, or flooding from heavy-rain events, which is what North Carolina saw last week. Even people who have personally experienced flooding sometimes drop their policies, Pralle said, adding that “if people have lived in a place where it hasn’t flooded in decades, they lose that memory of what can happen and what kind of losses they might suffer.”
Those who do buy flood insurance usually live in areas prone to flooding. The result is a system in which the risk is not evenly spread out, making flood-insurance premiums hugely pricey—Pralle likened it to a health-insurance system in which only the sick buy coverage. Some countries organize their disaster-insurance programs so everyone pays a flat rate, Kousky explained. In the United States, that would mean someone living on Florida’s coastline would pay the same premium as someone living on the top of a mountain. That’s a tough sell for many Americans, and overhauling the National Flood Insurance Program, which is saddled with debt, would be politically contentious.
Those without flood insurance will need to rely on a “patchwork” system of federal aid, loans, and charity, Kousky said, as they recover from Helene. One option is accepting government loans, but she noted that many people are not in a position to take on more debt after a hurricane—and their applications may be denied too. FEMA disaster-assistance grants are another pathway, and most of them do not need to be repaid—but those are “just an emergency stopgap,” Kousky said. They’re not designed to fully help people recover, usually providing only a few thousand dollars for each household—a fraction of what residents would need to rebuild.
The process of recovering from Helene is just beginning. Still, hurricane season is not over for the rest of the country, and FEMA currently does not have enough funding to make it through the rest of the season. Last week, President Joe Biden signed a short-term spending bill authorizing another $16 billion for the agency, but further funding would need to come from Congress, which is currently in recess until after the election.
So much of the response following disasters can feel piecemeal and reactive, Pralle said. Insurance is important—but not the full story. “Every dollar we put into prevention is going to be a lot more efficiently spent,” she explained. In a world reshaped by climate change, “this idea that there’s safe places you can go hide is unrealistic.”