New Dwarf Planet Found in Our Solar System
A new face has been added to the solar system’s family portrait: Scientists have discovered a new dwarf planet looping around the sun in the region beyond Pluto.
More…
New Dwarf Planet Found in Our Solar System
A new face has been added to the solar system’s family portrait: Scientists have discovered a new dwarf planet looping around the sun in the region beyond Pluto.
More…
> The dwarf planet, called 2014 UZ224, measures about 330 miles (530 kilometers) across and is located about 8.5 billion miles (13.7 billion km) from the sun, NPR reported today (Oct. 11). For comparison, Pluto’s largest moon, Charon, is about 750 miles (1,200 km) in diameter, and reaches a maximum distance of about 4.5 billion miles (7.3 billion km) from the sun. A year on 2014 UZ224 (the time it takes the dwarf planet to orbit the sun) is about 1,100 Earth years. One Pluto year, for c is about 248 Earth years.
Not a dwarf planet yet, not at that small size.
There are 29 dwarf planet candidates with a diameter larger than 600 km, and 45 dwarf planet candidates with a diameter 500 to 600 km, now 46.
The large distance to this new object, and the slowdown in Kuyper Belt and Scattered Disk discoveries means that we’re getting close to having found all of the large Kuyper Belt objects.
mollwollfumble said:
> The dwarf planet, called 2014 UZ224, measures about 330 miles (530 kilometers) across and is located about 8.5 billion miles (13.7 billion km) from the sun, NPR reported today (Oct. 11). For comparison, Pluto’s largest moon, Charon, is about 750 miles (1,200 km) in diameter, and reaches a maximum distance of about 4.5 billion miles (7.3 billion km) from the sun. A year on 2014 UZ224 (the time it takes the dwarf planet to orbit the sun) is about 1,100 Earth years. One Pluto year, for c is about 248 Earth years.Not a dwarf planet yet, not at that small size.
There are 29 dwarf planet candidates with a diameter larger than 600 km, and 45 dwarf planet candidates with a diameter 500 to 600 km, now 46.
The large distance to this new object, and the slowdown in Kuyper Belt and Scattered Disk discoveries means that we’re getting close to having found all of the large Kuyper Belt objects.
“the new dwarf planet was discovered using an instrument called the Dark Energy Camera (DECam). Part of the Dark Enery Survey (DES) includes taking images of a few small patches of the sky “roughly” once per week, according to the mission website, and that’s what made this new discovery possible. While stars and galaxies appear in the same place in the sky, an object that is relatively close to Earth and orbiting the sun would appear to move. A few years ago, Gerdes asked some visiting undergraduates to look for unidentified solar system objects in the galaxy map. The challenge was slightly difficult because the repeated observations would take place at irregular intervals. It took two years to confirm the detection of 2014 UZ224 and while its exact orbital path is still unclear, the scientists behind the discovery say they think that 2014 UZ224 is the third most-distant object in the solar system.”
Third most distant, if true, is very distant indeed. In terms of semi-major axis, Sedna is now the eighth most distant.
Details of 2014 UZ224 are at http://www.minorplanetcenter.net/db_search/show_object?object_id=2014+UZ224&commit=Show
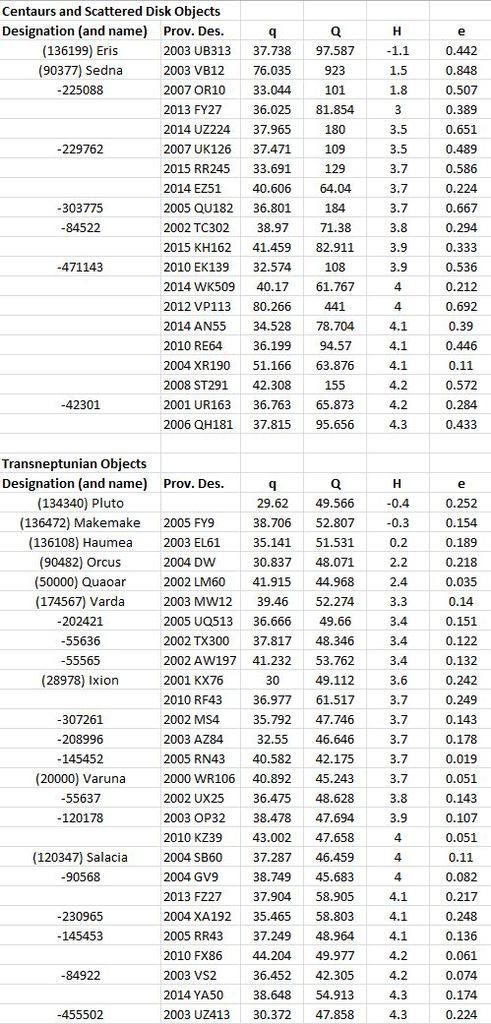
2014 UZ224
Semimajor axis = 108.9 AU.
Eccentricity = 0.65.
Absolute magnitude 3.5.
Compare with Sedna.
Semimajor axis = 499.4 AU
Eccentricity = 0.85.
Absolute magnitude 1.5.
According to that, Sedna is both much bigger and much further, on average. How to they come up with “third most distant”?
Top dwarf planet candidates, excluding Ceres and Charon. The biggest have the highest brightness (lowest H magnitude). q and Q are the closest and furthest approaches in Astronomical Units (Earth is 1). e is the eccentricity (0 is circle and 1 is parabola).
The new one 2014 UZ224 is 5th from the top among the Scattered Disk Objects.